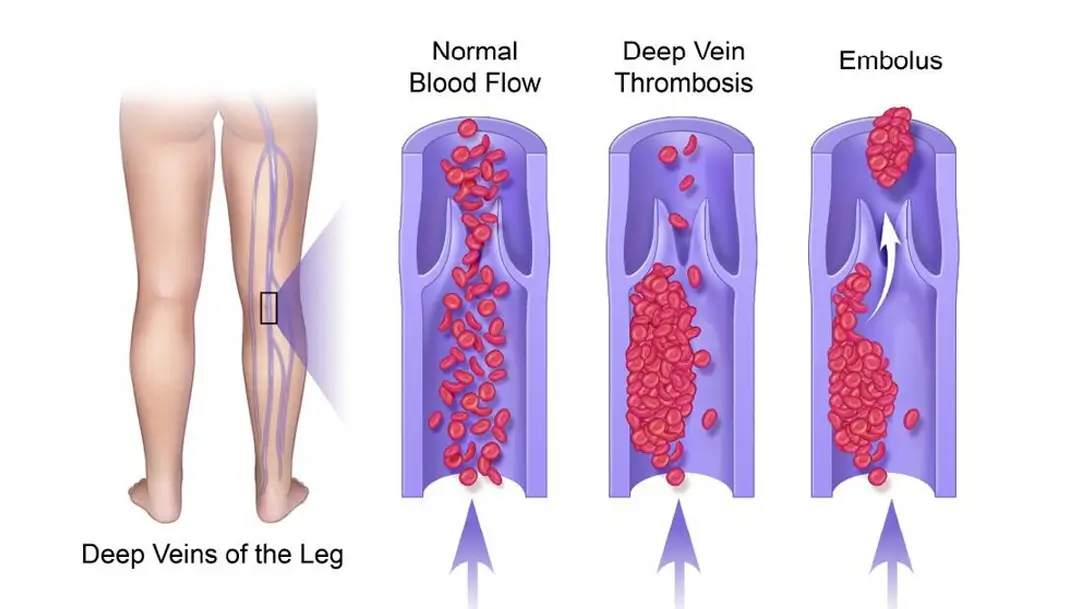
DVT occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs.
It can be very serious because blood clots in your veins can break loose, travel through your bloodstream, and lodge in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism).
Symptoms:
- Swelling of affected leg
- Pain
- Redness in affected leg
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid pulse
- Feeling lightheaded or fainting
Risk Factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
- Inheriting a blood-clotting disorder
- Prolonged bed rest – during/after hospital stay or paralysis
- Pregnancy
- Injury or surgery
- Birth control pills
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- Cancer
- Family history of DVT
- Sitting for long periods of time (such as when driving or flying)
Prevention Tips:
- Avoid sitting still for long durations
- While traveling – stand/walk occasionally
- Don't sit with legs crossed
- Perform heel-raising exercises
- Make lifestyle changes
- Exercise regularly
Treatment:
- Blood Thinners (Anticoagulation)
- Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (CDT)
- Compression stockings
- Surgery to remove the clot if necessary